4. Varde
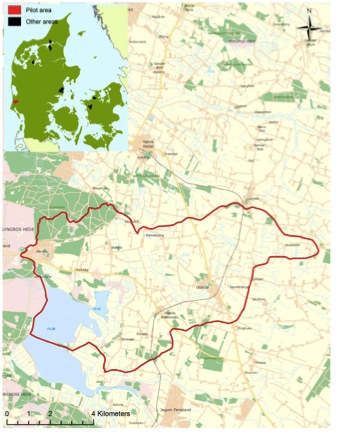
The pilot area Varde covers an area of 6282 ha and belongs to Varde municipality in western Jutland. Varde represents the pilot area with the highest nature area outside agriculture. This is due to i.a. Blaabjerg dune plantation in the northwestern part and the newly restored Filsoe (year 2012) in the southwestern part of the area – in all 29.6 % of the area is set aside to nature. The terrain is highly variable from east to west, and it is also the hilly, wet, and sandy parts in the west that represents nature outside agriculture, whereas the more fertile east is dominated by agriculture.
Download a complete PDF version here.
Map: Geographical location of the pilot area Varde.
LAND USE
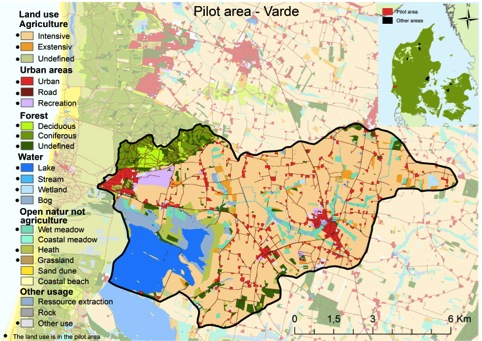
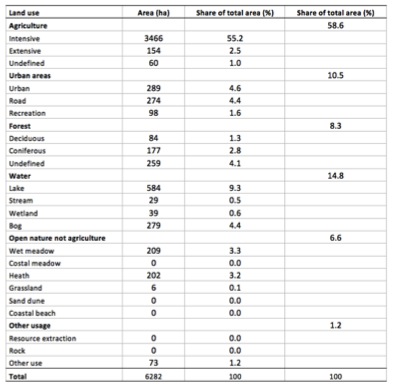
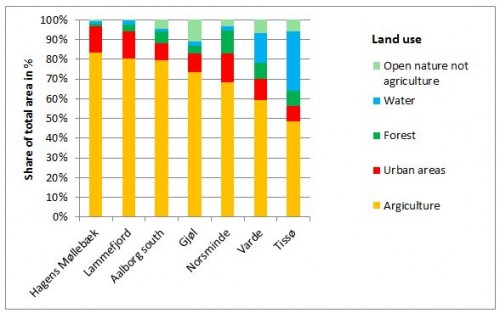
The main land use in Varde is intensive agriculture (55.2 %) followed by nature areas outside agriculture such as water, forest, and open nature (29.7 %) and urban areas (10.5 %) (map and table). The area hereby represents – together with Tissoe (43 %) – those areas with the largest portion of nature of all pilot areas (figure). The large nature area is mainly due to Blaabjerg dune plantation in the northwestern part and the newly restored Filsoe (year 2012).
Land use is illustrated on the map and the belonging table for Varde below. Furthermore, land use for the 7 pilot areas is illustrated in the figure.
Map: Land use in the pilot area Varde in 10×10 meters resolution.
Table: Land use in Aalborg south in hectare (ha) and share of total area in percent (%).
Figure: Land use in the 7 pilot areas described as share of total area in percent (%). The pilot areas are listed to % agriculture.
SOIL
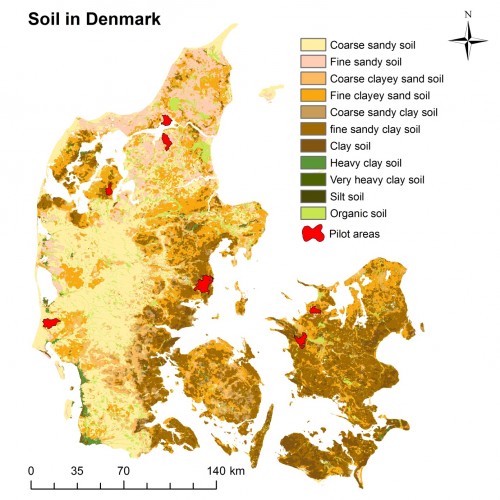
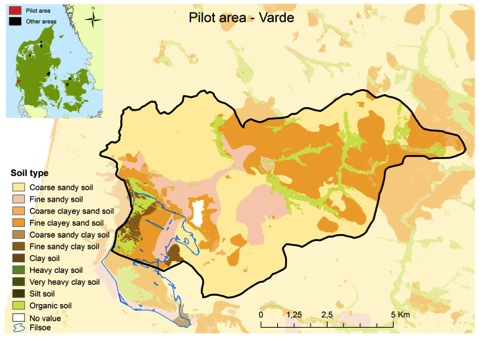
Overall the western soils of Denmark contain a high sand percentage whereas the eastern parts are dominated by the more heavy soils – clay (map 1). Varde is located in western Denmark and is also dominated by the sandy soils (89.7 %) (map 2 and table).
The soil types of the pilot area are illustrated on map 2 and the belonging table below.
Map 1: Soil type in Denmark.
Map 2: Distribution of soil types in the pilot area Varde in 30.4×30.4 meters resolution.
Table: Distribution of soil types in the pilot area Varde in hectare (ha) and share of the total area in percent (%).
TOPOGRAPHY
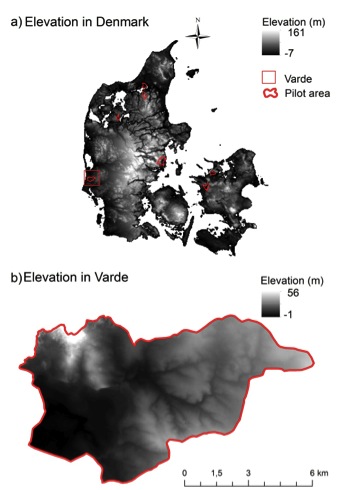
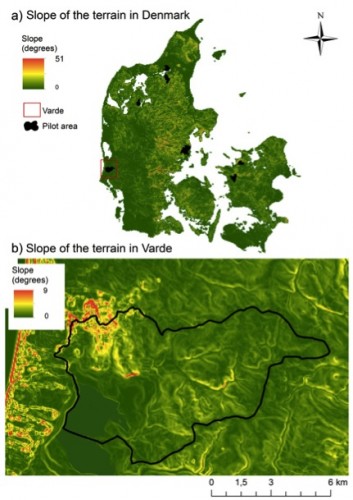
The elevation of Varde varies from -1 to 56 meters above the sea level (map 1), and a slope of the terrain from 0-5 degrees (map 2). Thereby, Varde is a relatively flat area except from the more hilly terrain in the northwestern part of the area (map 1b) and steep slopes near watercourses. The terrain, high sand percentage in the soil, and the high wetness of the area (all factors which are unfavorable for agriculture) are important drivers of the land use.
Map 1: Elevation in Denmark (a) and in the pilot area Varde (b) in 48×48 meters resolution.
Map 2: Slope of the terrain in Denmark (a) and in the pilot area Varde (b) in 48×48 meters resolution
HYDROLOGY
Wetness is here illustrated by the topographical wetness index. The wetness index calculates how much water a given point in the terrain potential can receive (the size of the catchment) in relation to its ability to drain itself (slope of the terrain). The index expresses the ability of the point to accumulate water. It is based alone on placement of the point in the terrain and the shape of the terrain, and does not include other factors such as soil type, precipitation, etc.
The pilot area is delineated by the water catchment defined by the watercourse system in Varde. It is a relatively wet area, especially in the southwestern parts.
Map: Topographical wetness index in Denmark (a) and in the pilot area Varde (b) in 48×48 meters resolution





 Danish
Danish